In order to safeguard networks, devices, programs, and data from theft, attack, damage, tampering, and unauthorised access, a variety of technologies, procedures, and practices have been developed.
System, network, program, and data-related technologies are all included in the term “Cyber”. Additionally, security is concerned with safeguarding data, applications, networks, and systems. To gain more knowledge enroll in our Cyber Security Certification.
Cybersecurity, no doubt, has a bright future. And here are some predictions made by a few industry experts that you need to know about Cyber security for 2024.
1-The supply chain and geopolitical risk will dominate cybersecurity

Source: etftrends.com
Numerous geopolitical concerns continue to have an effect on organisations on a global scale; by 2024, many of these challenges will become supply chain vulnerabilities. On partners and trustworthy third parties, the virus, political and social unrest, worries about online privacy & ethics, and climate change all have an impact.
This increases the likelihood of malware assaults, attacks on public clouds, attacks on the availability and security of systems, including distributed denial of service (DDoS), and information loss or theft for businesses and their supply chains.
Organisations must put in place effective security measures to reduce any supply chain threats they may be exposed to. Addressing socio-technical concerns about supply chain cybersecurity will be required in 2024.
These hazards are not largely caused by IT security flaws, but rather problems with purchasing gear and software, business continuity, and transportation.
2-With new building designs, security will rise
Security employees must be able to quickly identify vulnerabilities caused by either new IT efforts, like moving to the cloud or increasing the use of modern uses, or developing threats in order to identify risks and address them.
Integrated cybersecurity platforms defined by their primary data lake-oriented features are being developed by large security corporations as cybersecurity mesh architectures (CSMAs). These systems aim to provide a single console, integrated orchestration, automation, machine learning (ML), and support for third-party integration.
These platforms develop as new features and integrations are introduced across time in response to shifting client expectations. Enterprises will benefit from CSMAs by having an easier time managing multiple point items.
3-Business will require DevSecOps
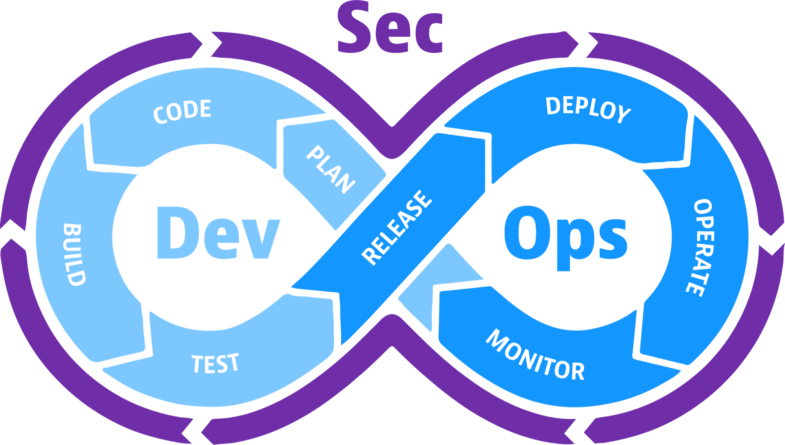
Source: dynatrace.com
A wide attack surface is being opened up for malicious actors by the ongoing development and variety of API and application installations.
Therefore, organisations must see the safe creation and implementation of APIs and apps as being of the utmost importance to their operations. Utilising DevSecOps methodologies, security must be integrated into the application delivery processes in order to accomplish this efficiently without slowing down velocity.
The distinction between infrastructure and apps is muddled by DevSecOps. Considerations for application and data protection go in tandem with those related to infrastructure security, as security teams will discover.
Attackers are taking advantage of flaws in this crucial component to access application components, confidential data, and source code. For a comprehensive DevSecOps strategy in 2024, security personnel will progressively connect security and devops processes. Automation and the development process must both incorporate security.
4-Zero trust will be a key component of risk management
Continually evaluated risk and trust factors based on identities and context are used in place of implicit trust in zero-trust architectures (ZTA), which also changes to risk-optimise security postures. As a result, each request to use a ZTA resource must include a risk assessment, and trust must be explicit.
The risk assessment considers a number of signals, including the location of the device, the plausibility of the user’s statement, the cleanliness of the device, threat information, the time of day, the day of the week, and the data vulnerability of the app being requested.
Access is only allowed when the estimated risk is lower than the benefit of expanding the access. Enterprises will employ ZTA more often in 2024 to improve and risk-optimise the organisation’s entire security posture.
5-Data-centric cybersecurity will be necessary in a “data data everywhere” future

Source: securityindustry.org
The amount of data is increasing both within and outside the organisations that collect it and first take responsibility for its safety. Since many businesses haven’t made constant monitoring of it a top priority, there is essentially no insight into this data.
“Storage of data without visibility for the organisation,” is how dark data is defined. Estimates of the percentage of data that only an organisation maintains are secret vary from 56% to over 80%. These shadowy data are harbouring unknown data risks.
In particular, where regulations may directly conflict with business requirements, privacy and security compliance within data warehouses and big data/advanced analytical processes are becoming more and more crucial.
Data-centric security is essential for data protection in the always-on, “data data everywhere” environment of today. By 2024, businesses must focus on integrating a data-centric approach into their fundamental security architecture.
6-Human-operated ransomware will become a greater risk
As more and more sophisticated attacks continue to surface, human-operated ransomware is becoming an inescapable issue. Security teams must adapt their defence strategies in response to these ransomware gangs’ more sophisticated tactics.
Preattack and peri-attack stages of a ransomware attack are when the majority of mitigation takes place.
Once the intruder has successfully entered, detection controls are essential for recognising anomalous attacker behaviour.
In order to provide effective protection against sophisticated ransomware, organisations require a mix of multiple detection and prevention mechanisms, a dependable backup/recovery procedure, and a program of core security practices and processes.
The appropriate balancing act of several measures is necessary to maintain a robust endpoint security ecosystem; no single methodology or piece of legislation can serve as a “silver bullet.D Manufacturers of EDR and endpoint protection platforms (EPP) are starting to offer Extended detection and Response (XDR).
7-Flexible protection both against new and old threats will be needed for workloads and endpoints

Source: blog.morphisec.com
Endpoints are still one of the main targets for knowledgeable hackers. Instead of only stealing sensitive data, attackers are also using endpoints as a jumping off point for more profitable attacks like ransomware and business email infiltration.
A growing number of gadgets, such as IoT and virtual personal aides, are also a problem for businesses since they need access to their networks, applications, or data. These include personal devices used by employees away from corporate networks.
Security professionals should assess malware protection designs across networks, client endpoints, and server endpoints in 2024 as the threat surface continues to grow.
Solutions like managed threat detection (MTD) and endpoint preparedness and response (EDR) can offer both prevention and detection and mitigation capabilities that can assist shorten the time it takes to recover from a successful assault.
