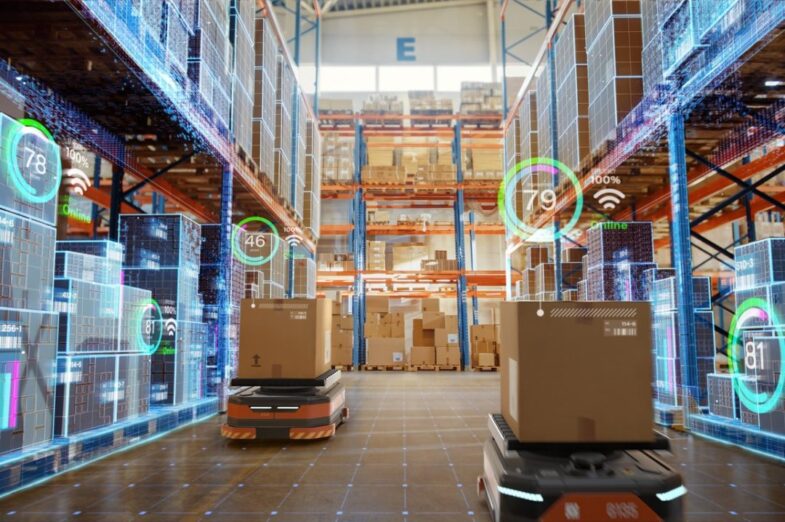
In today’s rapidly evolving retail landscape, the efficient management of the supply chain has emerged as the linchpin for success. Retailers worldwide are embracing cutting-edge technologies and automation to streamline their operations, ensuring that products are efficiently delivered to the end consumer.
This article delves into the pivotal role that technology plays in every facet of retail supply chain management, explores the benefits and challenges associated with these innovations, and speculates on the promising future of this dynamic field.
The Role of Technology in Retail Supply Chain Management

Source: indianretailer.com
Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is crucial to prevent stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and maintain healthy cash flows. The implementation of various technologies has revolutionized this aspect of retail supply chain management.
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) and barcode scanning have become the cornerstones of modern inventory management. RFID tags enable real-time monitoring of stock levels, providing unparalleled visibility into inventory locations and quantities. Barcode scanning, on the other hand, ensures pinpoint accuracy during stock movement, reducing errors and enhancing overall inventory control.
Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is fundamental for retailers to anticipate consumer trends, optimize stock levels, reduce carrying costs, and swiftly respond to shifting customer preferences. In this realm, machine learning algorithms and big data analytics have been game-changers.
Machine learning and big data analytics empower retailers to analyze vast amounts of historical and real-time data. This allows them to predict consumer trends with greater precision, enabling data-driven decision-making. Such insights can lead to more accurate demand forecasts, which in turn enable retailers to optimize their inventory, reducing carrying costs and enhancing profitability.
Order Processing and Fulfillment
Source: tenaxxlogistics.com
Automation has significantly improved order processing and fulfillment, creating a more streamlined and efficient supply chain.
Automated order systems allow for seamless order placement and tracking. With a few clicks, customers can place orders, and these orders can be tracked in real-time. This not only enhances the customer experience but also reduces order processing times and minimizes the potential for errors.
Additionally, robotics has found a valuable place in warehousing and distribution centers. These machines can swiftly and accurately pick and pack orders, leading to quicker and more accurate order fulfillment. The result is higher customer satisfaction, as products are delivered promptly and with fewer errors.
Deduction Management
Deduction management is a critical but often overlooked component of supply chain management. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining healthy relationships with suppliers. Technology-driven deduction resolution systems have streamlined the process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving deductions, which include chargebacks, shortages, and pricing discrepancies.
These systems reduce financial losses and ensure fair and transparent interactions with suppliers, ultimately fostering better collaboration and trust. In a highly competitive market, maintaining healthy supplier relationships can be a key differentiator.
Check out best in class AR Deduction Management Software from iNymbus.
Benefits of Technology and Automation

Source: telecomtv.com
The adoption of technology and automation in retail supply chain management offers a multitude of compelling advantages:
- Improved Efficiency: Automation reduces manual tasks and minimizes errors, ultimately speeding up processes and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
- Cost Reduction: Optimized inventory, faster order fulfillment, and reduced deductions lead to significant cost savings. Retailers can allocate resources more efficiently.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Technology-driven systems improve data accuracy, reducing discrepancies and minimizing costly mistakes.
- Better Customer Service: Efficient supply chain management ensures timely product availability, reducing lead times, and improving customer satisfaction. Retailers that can consistently meet customer demands enjoy a competitive edge in the market.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of incorporating technology and automation are clear, retailers must also address several challenges:
- Initial Investment Costs: Implementing technology and automation requires a significant upfront investment. Retailers need to carefully assess their budget and ROI to determine the feasibility of such implementations.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Many retailers have legacy systems in place. Integrating new technology with existing systems can be complex and requires meticulous planning to ensure a smooth transition.
- Data Security and Privacy: The handling of sensitive customer and supplier data necessitates robust security measures to safeguard against data breaches and privacy violations.
- Workforce Training and Adaptation: Employees need adequate training to adapt to new technologies and processes. Ensuring that the workforce is comfortable with the new tools is essential to realizing the full potential of these innovations.
The Future of Retail Supply Chain Management

Source: business-reporter.co.uk
The future of retail supply chain management promises to be even more exciting, with several trends and innovations on the horizon:
- Emerging Technologies: The Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain technology are poised to further enhance tracking and transparency within the supply chain. IoT devices can provide real-time data on the location and condition of products, while blockchain can offer a secure and immutable record of every transaction within the supply chain.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Retailers are increasingly focusing on green supply chain practices to reduce their environmental footprint. Sustainability practices can include eco-friendly packaging, energy-efficient transportation, and reducing waste in the supply chain.
- AI’s Role: Artificial Intelligence (AI) will continue to play a pivotal role in optimizing supply chain processes and enhancing decision-making. AI can help identify patterns, optimize routes for transportation, and even predict potential disruptions in the supply chain, allowing retailers to proactively address issues before they become major problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, technology and automation have become indispensable tools for retailers aiming to stay competitive in the dynamic world of supply chain management. The benefits, although accompanied by challenges, are too significant to ignore. As technology continues to advance, retailers must embrace these innovations to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ultimately deliver better experiences to their customers.
The future of retail supply chain management is indeed a promising one, marked by sustainability, increased reliance on cutting-edge technologies, and a commitment to providing superior service to consumers.
By harnessing the power of these innovations, retailers can position themselves as industry leaders, capable of thriving in an ever-evolving market landscape. The future is bright, and retailers who adapt and invest wisely will undoubtedly reap the rewards.
